NAMES
TAXONOMY
Namibia
Issued:
Stamp:
Aepyceros melampus
South Africa
Issued:
Stamp:
Aepyceros melampus
Angola
Issued:
Stamp:
Aepyceros melampus
Namibia
Issued:
Stamp:
Aepyceros melampus
South Africa
Issued:
Stamp:
Aepyceros melampus
Angola
Issued:
Stamp:
Aepyceros melampus
Namibia
Issued:
Stamp:
Aepyceros melampus
South Africa
Issued:
Stamp:
Aepyceros melampus
Angola
Issued:
Stamp:
Aepyceros melampus
Genus species: Aepyceros melampus
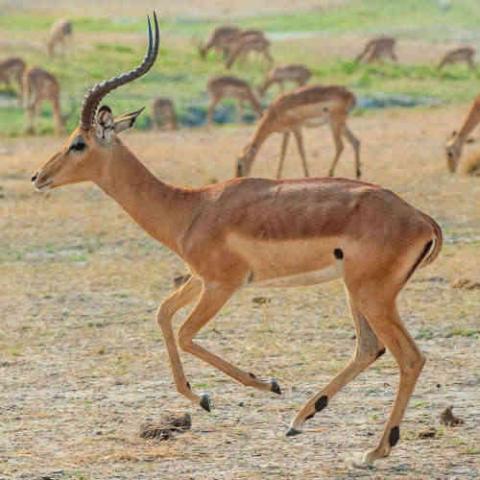
The impala or rooibok (Aepyceros melampus) is a medium-sized antelope found in eastern and southern Africa. The only extant member of the genus Aepyceros, and tribe Aepycerotini, it was first described to Europeans by German zoologist Hinrich Lichtenstein in 1812. Two subspecies are recognized—the grassland-dwelling common impala (sometimes referred to as the Kenyan impala), and the larger and darker black-faced impala, which lives in slightly more arid, scrubland environments. The impala reaches 70–92 cm (28–36 in) at the shoulder and weighs 40–76 kg (88–168 lb). It features a glossy, reddish brown coat. The male's slender, lyre-shaped horns are 45–92 cm (18–36 in) long.
Active mainly during the day, the impala may be gregarious or territorial depending upon the climate and geography. Three distinct social groups can be observed: the territorial males, bachelor herds and female herds. The impala is known for two characteristic leaps that constitute an anti-predator strategy. Browsers as well as grazers, impala feed on monocots, dicots, forbs, fruits and acacia pods (whenever available). An annual, three-week-long rut takes place toward the end of the wet season, typically in May. Rutting males fight over dominance, and the victorious male courts females in oestrus. Gestation lasts six to seven months, following which a single calf is born and immediately concealed in cover. Calves are suckled for four to six months; young males—forced out of the all-female groups—join bachelor herds, while females may stay back.
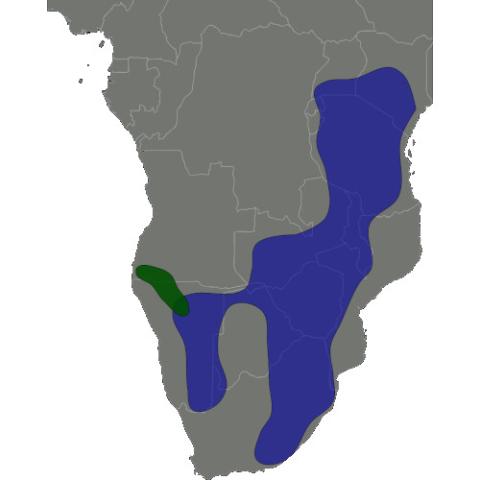
The impala is found in woodlands and sometimes on the interface (ecotone) between woodlands and savannahs; it inhabits places near water. While the black-faced impala is confined to southwestern Angola and Kaokoland in northwestern Namibia, the common impala is widespread across its range and has been reintroduced in Gabon and southern Africa. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) classifies the impala as a species of least concern; the black-faced subspecies has been classified as a vulnerable species, with fewer than 1,000 individuals remaining in the wild as of 2008.
Etymology
The first attested English name, in 1802, was palla or pallah, from the Tswana phala 'red antelope'; the name impala, also spelled impalla or mpala, is first attested in 1875, and is directly from Zulu. Its Afrikaans name, rooibok 'red buck', is also sometimes used in English.
The scientific generic name Aepyceros (lit. ‘high-horned’) comes from Ancient Greek αἰπύς (aipus, 'high, steep') + κέρας (keras, 'horn'); the specific name melampus (lit. ‘black-foot’) from μελάς (melas, 'black') + πούς (pous, 'foot').
Description
The impala is a medium-sized, slender-bodied antelope, comparable to the kob, puku and Grant's gazelle in size and build. The head-and-body length is around 130 cm (51 in). Males reach approximately 75–92 cm (30–36 in) at the shoulder, while females are 70–85 cm (28–33 in) tall. Males typically weigh 53–76 kg (117–168 lb) and females 40–53 kg (88–117 lb). Sexually dimorphic, females are hornless and smaller than males. Males grow slender, lyre-shaped horns 45–92 cm (18–36 in) long. The horns, strongly ridged and divergent, are circular in section and hollow at the base. Their arch-like structure allows interlocking of horns, which helps a male throw off his opponent during fights; horns also protect the skull from damage.
The glossy coat of the impala shows two-tone coloration – the reddish brown back and the tan flanks; these are in sharp contrast to the white underbelly. Facial features include white rings around the eyes and a light chin and snout. The ears, 17 cm (6.7 in) long, are tipped with black. Black streaks run from the buttocks to the upper hindlegs. The bushy white tail, 30 cm (12 in) long, features a solid black stripe along the midline. The impala's coloration bears a strong resemblance to the gerenuk, which has shorter horns and lacks the black thigh stripes of the impala. The impala has scent glands covered by a black tuft of hair on the hindlegs. 2-Methylbutanoic Acid and 2-Nonanone have been identified from this gland. Sebaceous glands concentrated on the forehead and dispersed on the torso of dominant males are most active during the mating season, while those of females are only partially developed and do not undergo seasonal changes. There are four nipples.
Of the subspecies, the black-faced impala is significantly larger and darker than the common impala; melanism is responsible for the black coloration. Distinctive of the black-faced impala is a dark stripe, on either side of the nose, that runs upward to the eyes and thins as it reaches the forehead. Other differences include the larger black tip on the ear, and a bushier and nearly 30% longer tail in the black-faced impala.
The impala has a special dental arrangement on the front lower jaw similar to the toothcomb seen in strepsirrhine primates, which is used during allogrooming to comb the fur on the head and the neck and remove ectoparasites.
Ecology and behavior
The impala is diurnal (active mainly during the day), though activity tends to cease during the hot midday hours; they feed and rest at night. Three distinct social groups can be observed – the territorial males, bachelor herds and female herds. The territorial males hold territories where they may form harems of females; territories are demarcated with urine and feces and defended against juvenile or male intruders. Bachelor herds tend to be small, with less than 30 members. Individuals maintain distances of 2.5–3 m (8.2–9.8 ft) from one another; while young and old males may interact, middle-aged males generally avoid one another except to spar. Female herds vary in size from 6 to 100; herds occupy home ranges of 80–180 ha (200–440 acres; 0.31–0.69 sq mi). The mother–calf bond is weak, and breaks soon after weaning; juveniles leave the herds of their mothers to join other herds. Female herds tend to be loose and have no obvious leadership. Allogrooming is an important means of social interaction in bachelor and female herds; in fact, the impala appears to be the only ungulate to display self-grooming as well as allogrooming. In allogrooming, females typically groom related impalas, while males associate with unrelated ones. Each partner grooms the other six to twelve times.
Social behavior is influenced by the climate and geography; as such, the impala are territorial at certain times of the year and gregarious at other times, and the length of these periods can vary broadly among populations. For instance, populations in southern Africa display territorial behavior only during the few months of the rut, whereas in eastern African populations, territoriality is relatively minimal despite a protracted mating season. Moreover, territorial males often tolerate bachelors, and may even alternate between bachelorhood and territoriality at different times of the year. A study of impala in the Serengeti National Park showed that in 94% of the males, territoriality was observed for less than four months.
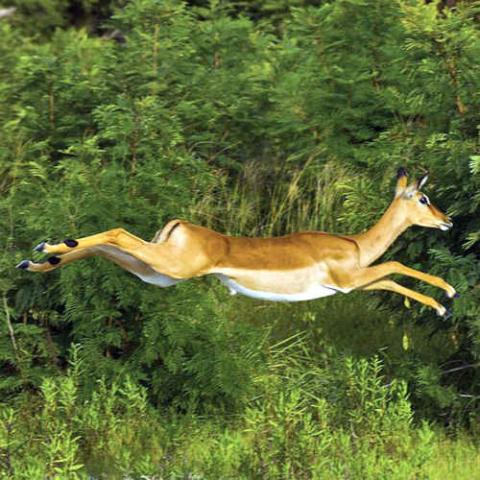
The impala is an important prey species for Africa's large carnivores, such as cheetahs, leopards, wild dogs, lions, hyenas, crocodiles and pythons. The antelope displays two characteristic leaps – it can jump up to 3 m (9.8 ft), over vegetation and even other impala, covering distances of up to 10 m (33 ft); the other type of leap involves a series of jumps in which the animal lands on its forelegs, moves its hindlegs mid-air in a kicking fashion, lands on all fours (stotting) and then rebounds. It leaps in either manner in different directions, probably to confuse predators. At times, the impala may also conceal itself in vegetation to escape the eye of the predator. The most prominent vocalization is the loud roar, delivered through one to three loud snorts with the mouth closed, followed by two to ten deep grunts with the mouth open and the chin and tail raised; a typical roar can be heard up to 2 km (1.2 mi) away. Scent gland secretions identify a territorial male. Impalas are sedentary; adult and middle-aged males, in particular, can hold their territories for years.
Parasites
Common ixodid ticks collected from impala include Amblyomma hebraeum, Boophilus decoloratus, Hyalomma marginatum, Ixodes cavipalpus, Rhipicephalus appendiculatus and R. evertsi. In Zimbabwe, heavy infestation by ticks such as R. appendiculatus has proved to be a major cause behind the high mortality of ungulates, as they can lead to tick paralysis. Impala have special adaptations for grooming, such as their characteristic dental arrangement, to manage ticks before they engorge; however, the extensive grooming needed to keep the tick load under control involves the risk of dehydration during summer, lower vigilance against predators and gradual wearing out of the teeth. A study showed that impala adjust the time devoted to grooming and the number of grooming bouts according to the seasonal prevalence of ticks.
Impala are symbiotically related to oxpeckers, which feed on ticks from those parts of the antelope's body which the animal cannot access by itself (such as the ears, neck, eyelids, forehead and underbelly). The impala is the smallest ungulate with which oxpeckers are associated. In a study it was observed that oxpeckers selectively attended to impala despite the presence of other animals such as Coke's hartebeest, Grant's gazelle, Thomson's gazelle and topi. A possible explanation for this could be that because the impala inhabits woodlands (which can have a high density of ticks), the impala could have greater mass of ticks per unit area of the body surface. Another study showed that the oxpeckers prefer the ears over other parts of the body, probably because these parts show maximum tick infestation. The bird has also been observed to perch on the udders of a female and pilfer its milk.
Lice recorded from impala include Damalinia aepycerus, D. elongata, Linognathus aepycerus and L. nevilli; in a study, ivermectin (a medication against parasites) was found to have an effect on Boophilus decoloratus and Linognathus species, though not on Damalinia species. In a study of impala in South Africa, the number of worms in juveniles showed an increase with age, reaching a peak when impala turned a year old. This study recorded worms of genera such as Cooperia, Cooperoides, Fasciola, Gongylonema. Haemonchus, Impalaia, Longistrongylus and Trichostrongylus; some of these showed seasonal variations in density.
Impala show high frequency of defensive behaviors towards flying insects. This is probably the reason for Vale 1977 and Clausen et al 1998 only finding trace levels of feeding by Glossina (tsetse fly) upon impala.
Theileria of impala in Kenya are not cross infectious to cattle: Grootenhuis et al 1975 were not able to induce cattle infection and Fawcett et al 1987 did not find it naturally occurring.
Distribution and habitat
The impala inhabits woodlands due to its preference for shade; it can also be found on the interface (ecotone) between woodlands and savannahs. Places near water sources are preferred. In southern Africa, populations tend to be associated with Colophospermum mopane and Acacia woodlands. Habitat choices differ seasonally – Acacia senegal woodlands are preferred in the wet season, and A. drepanolobium savannahs in the dry season. Another factor that could influence habitat choice is vulnerability to predators; impala tend to keep away from areas with tall grasses as predators could be concealed there. A study found that the reduction of woodland cover and creation of shrublands by the African bush elephants has favored impala population by increasing the availability of more dry season browse. Earlier, the Baikiaea woodland, which has now declined due to elephants, provided minimum browsing for impala. The newly formed Capparis shrubland, on the other hand, could be a key browsing habitat. Impala are generally not associated with montane habitats; however, in KwaZulu-Natal, impala have been recorded at altitudes of up to 1,400 m (4,600 ft) above sea level.
The historical range of the impala – spanning across southern and eastern Africa – has remained intact to a great extent, although it has disappeared from a few places, such as Burundi. The range extends from central and southern Kenya and northeastern Uganda in the east to northern KwaZulu-Natal in the south, and westward up to Namibia and southern Angola. The black-faced impala is confined to southwestern Angola and Kaokoland in northwestern Namibia; the status of this subspecies has not been monitored since the 2000s. The common impala has a wider distribution, and has been introduced in protected areas in Gabon and across southern Africa.
Threats and conservation
The International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) classifies the impala as a species of least concern overall. The black-faced impala, however, is classified as a vulnerable species; as of 2008, fewer than 1,000 were estimated in the wild. Though there are no major threats to the survival of the common impala, poaching and natural calamities have significantly contributed to the decline of the black-faced impala. As of 2008, the population of the common impala has been estimated at around two million. According to some studies, translocation of the black-faced impala can be highly beneficial in its conservation.
Around a quarter of the common impala populations occur in protected areas, such as the Okavango Delta (Botswana); Masai Mara and Kajiado (Kenya); Kruger National Park (South Africa); the Ruaha and Serengeti National Parks and Selous Game Reserve (Tanzania); Luangwa Valley (Zambia); Hwange, Sebungwe and Zambezi Valley (Zimbabwe). The rare black-faced impala has been introduced into private farms in Namibia and the Etosha National Park. Population densities vary largely from place to place; from less than one impala per sq km in Mkomazi National Park (Tanzania) to as high as 135 per sq km near Lake Kariba (Zimbabwe).
Reference: Wikipedia
Photo: Hein Waschefort, Arturo de Frias Marques, Jcwf