NAMES
TAXONOMY
South Africa
Issued:
Stamp:
Diceros bicornis
Republic of the Congo
Issued:
Stamp:
Diceros bicornis
Angola
Issued:
Stamp:
Diceros bicornis
South Africa
Issued:
Stamp:
Diceros bicornis
Republic of the Congo
Issued:
Stamp:
Diceros bicornis
Angola
Issued:
Stamp:
Diceros bicornis
South Africa
Issued:
Stamp:
Diceros bicornis
Republic of the Congo
Issued:
Stamp:
Diceros bicornis
Angola
Issued:
Stamp:
Diceros bicornis
Genus species (Animalia): Diceros bicornis
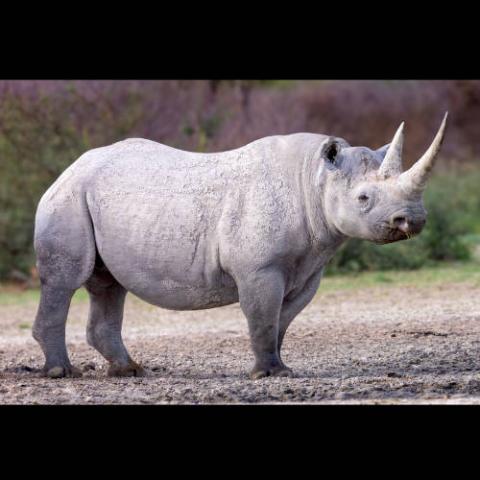
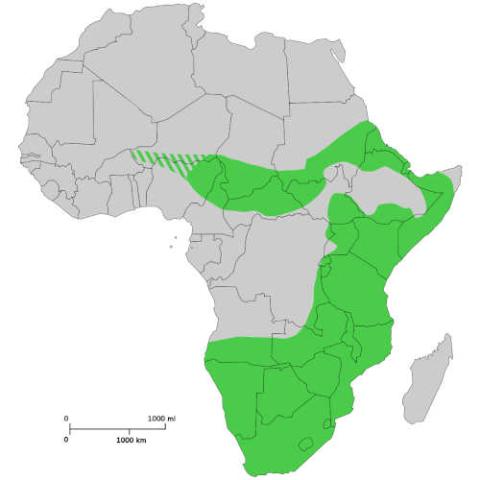
The black rhinoceros, black rhino or hook-lipped rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis) is a species of rhinoceros, native to eastern Africa and southern Africa, including Angola, Botswana, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Eswatini, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Although the species is referred to as black, its colors vary from brown to grey. It is the only extant species of the genus Diceros.
The other African rhinoceros is the white rhinoceros (Ceratotherium simum). The word "white" in the name "white rhinoceros" is often said to be a misinterpretation of the Afrikaans word wyd (Dutch wijd) meaning wide, referring to its square upper lip, as opposed to the pointed or hooked lip of the black rhinoceros. These species are now sometimes referred to as the square-lipped (for white) or hook-lipped (for black) rhinoceros.
The species overall is classified as critically endangered (even though the south-western black rhinoceros is classified as near threatened) and is threatened by multiple factors including poaching and habitat reduction. Three subspecies have been declared extinct, including the western black rhinoceros, which was declared extinct by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) in 2011. The IUCN estimates that there are 3,142 mature individuals remaining in the wild.
Taxonomy
The species was first named Rhinoceros bicornis by Carl Linnaeus in the 10th edition of his Systema naturae in 1758. The name means "double-horned rhinoceros". There is some confusion about what exactly Linnaeus conceived under this name as this species was probably based upon the skull of a single-horned Indian rhinoceros (Rhinoceros unicornis), with a second horn artificially added by the collector. Such a skull is known to have existed and Linnaeus even mentioned India as origin of this species. However he also referred to reports from early travelers about a double-horned rhino in Africa and when it emerged that there is only one, single-horned species of rhino in India, Rhinoceros bicornis was used to refer to the African rhinos (the white rhino only became recognized in 1812). In 1911 this was formally fixed and the Cape of Good Hope officially declared the type locality of the species.
Description
An adult black rhinoceros stands 132–180 cm (52–71 in) high at the shoulder and is 2.8–3.75 m (9.2–12.3 ft) in length. An adult typically weighs from 800 to 1,400 kg (1,760 to 3,090 lb), however unusually large male specimens have been reported at up to 2,896 kg (6,385 lb). The cows are smaller than the bulls. Two horns on the skull are made of keratin with the larger front horn typically 50 cm (20 in) long, exceptionally up to 135.9 cm (53.5 in).
The longest known black rhinoceros horn measured nearly 1.5 m (4.9 ft) in length. Sometimes a third, smaller horn may develop. These horns are used for defense, intimidation, and digging up roots and breaking branches during feeding. The black rhino is smaller than the white rhino and close in size to the Javan rhino of Indonesia. It has a pointed and prehensile upper lip, which it uses to grasp leaves and twigs when feeding, whereas the white rhinoceros has square lips used for eating grass. The black rhinoceros can also be distinguished from the white rhinoceros by its size, smaller skull, and ears; and by the position of the head, which is held higher than the white rhinoceros, since the black rhinoceros is a browser and not a grazer.
Their thick-layered skin helps to protect black rhinos from thorns and sharp grasses. Their skin harbors external parasites, such as mites and ticks, which may be eaten by oxpeckers and egrets. Such behavior was originally thought to be an example of mutualism, but recent evidence suggests that oxpeckers may be parasites instead, feeding on rhino blood. It is commonly assumed that black rhinos have poor eyesight, relying more on hearing and smell. However, studies have shown that their eyesight is comparatively good, at about the level of a rabbit. Their ears have a relatively wide rotational range to detect sounds. An excellent sense of smell alerts rhinos to the presence of predators.
Behavior
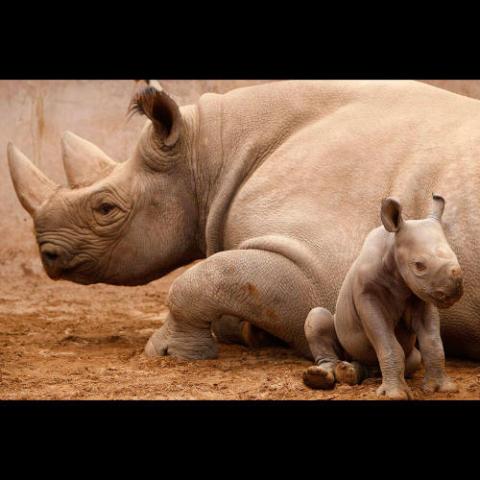
Black rhinos are generally thought to be solitary, with the only strong bond between a mother and her calf. In addition, bulls and cows have a consort relationship during mating, also subadults and young adults frequently form loose associations with older individuals of either sex. They are not very territorial and often intersect other rhino territories. Home ranges vary depending on season and the availability of food and water. Generally they have smaller home ranges and larger density in habitats that have plenty of food and water available, and vice versa if resources are not readily available. Sex and age of an individual black rhino influence home range and size, with ranges of cows larger than those of bulls, especially when accompanied by a calf. In the Serengeti home ranges are around 70 to 100 km2 (27 to 39 sq mi), while in the Ngorongoro it is between 2.6 to 58.0 km2 (1.0 to 22.4 sq mi). Black rhinos have also been observed to have a certain area they tend to visit and rest frequently called "houses" which are usually on a high ground level. These "home" ranges can vary from 2.6 km2 to 133 km2 with smaller home ranges having more abundant resources than larger home ranges.
Black rhinos in captivity and reservations sleep patterns have been recently studied to show that males sleep longer on average than females by nearly double the time. Other factors that play a role in their sleeping patterns is the location of where they decide to sleep. Although they do not sleep any longer in captivity, they do sleep at different times due to their location in captivity, or section of the park.
Black rhinos have a reputation for being extremely aggressive, and charge readily at perceived threats. They have even been observed to charge tree trunks and termite mounds. Black rhinos will fight each other, and they have the highest rates of mortal combat recorded for any mammal: about 50 percent of males and 30 percent of females die from combat-related injuries. Adult rhinos normally have no natural predators, due to their imposing size, thick skin, and deadly horns. However, adult black rhinos have fallen prey to crocodiles in exceptional circumstances. Calves and, very seldom, small sub-adults may be preyed upon by lions as well.
Black rhinos follow the same trails that elephants use to get from foraging areas to water holes. They also use smaller trails when they are browsing. They are very fast and can get up to speeds of 55 km per hour (34 mph) running on their toes.
While it was assumed all rhinoceros are short-sighted, a study involving black rhinoceros retinas suggests they have better eyesight than previously assumed.
Diet
Black rhinos are herbivorous browsers that eat leafy plants, twigs, branches, shoots, thorny wood bushes, small trees, legumes, fruit, and grass. The optimum habitat seems to be one consisting of thick scrub and bushland, often with some woodland, which supports the highest densities. Their diet can reduce the number of woody plants, which may benefit grazers (who focus on leaves and stems of grass), but not competing browsers (who focus on leaves, stems of trees, shrubs or herbs). It has been known to eat up to 220 species of plants. They have a significantly restricted diet with a preference for a few key plant species and a tendency to select leafy species in the dry season. The plant species they seem to be most attracted to when not in dry season are the woody plants. There are 18 species of woody plants known to the diet of the black rhinoceros, and 11 species that could possibly be a part of their diet too. Black rhinos also have a tendency to choose food based on quality over quantity, where researchers find more populations in areas where the food has better quality. Black rhinos show a preference for Acacia species, as well as plants in the family Euphorbiaceae.
In accordance with their feeding habit, adaptations of the chewing apparatus have been described for rhinos. The black rhinoceros has a two phased chewing activity with a cutting ectoloph and more grinding lophs on the lingual side. The black rhinoceros can also be considered a more challenging herbivore to feed in captivity compared to its grazing relatives. They can live up to 5 days without water during drought. Black rhinos live in several habitats including bushlands, Riverine woodland, marshes, and their least favorable, grasslands. Habitat preferences are shown in two ways, the amount of sign found in the different habitats, and the habitat content of home ranges and core areas. Habitat types are also identified based on the composition of dominant plant types in each area. Different subspecies live in different habitats including Vachellia and Senegalia savanna, Euclea bushlands, Albany thickets, and even desert. They browse for food in the morning and evening. They are selective browsers but, studies done in Kenya show that they do add the selection material with availability in order to satisfy their nutritional requirements. In the hottest part of the day they are most inactive- resting, sleeping, and wallowing in mud. Wallowing helps cool down body temperature during the day and protects against parasites. When black rhinos browse they use their lips to strip the branches of their leaves. Competition with elephants is causing the black rhinoceros to shift its diet. The black rhinoceros alters its selectivity with the absence of the elephant.
There is some variance in the exact chemical composition of rhinoceros horns. This variation is directly linked to diet and can be used as a means of rhino identification. Horn composition has helped scientists pinpoint the original location of individual rhinos, allowing for law enforcement to more accurately and more frequently identify and penalize poachers.
Reproduction
The adults are solitary in nature, coming together only for mating. Mating does not have a seasonal pattern but births tend to be towards the end of the rainy season in more arid environments.
When in season the cows will mark dung piles. Bulls will follow cows when they are in season; when she defecates he will scrape and spread the dung, making it more difficult for rival adult bulls to pick up her scent trail.
Courtship behaviors before mating include snorting and sparring with the horns among males. Another courtship behavior is called bluff and bluster, where the black rhino will snort and swing its head from side to side aggressively before running away repeatedly. Breeding pairs stay together for 2–3 days and sometimes even weeks. They mate several times a day over this time and copulation lasts for a half-hour.
The gestation period for a black rhino is 15 months. The single calf weighs about 35–50 kilograms (80–110 lb) at birth, and can follow its mother around after just three days. Weaning occurs at around 2 years of age for the offspring. The mother and calf stay together for 2–3 years until the next calf is born; female calves may stay longer, forming small groups. The young are occasionally taken by hyenas and lions. Sexual maturity is reached from 5 to 7 years old for females, and 7 to 8 years for males. The life expectancy in natural conditions (without poaching pressure) is from 35 to 50 years.
Threats
Today, there are various threats posed to black rhinos including habitat changes, illegal poaching, and competing species. Civil disturbances, such as war, have made mentionably negative effects on the black rhinoceros populations in since the 1960s in countries including, but not limited to, Chad, Cameroon, Rwanda, Mozambique, and Somalia. In the Addo Elephant National Park in South Africa, the African bush elephant (Loxodonta africana) is posing slight concern involving the black rhinoceroses who also inhabit the area. Both animals are browsers; however, the elephant's diet consists of a wider variety of foraging capacity, while the black rhinoceros primarily sticks to dwarf shrubs. The black rhinoceros has been found to eat grass as well; however, the shortening of its range of available food could be potentially problematic.
Black rhinos face problems associated with the minerals they ingest. They have become adjusted to ingesting less iron in the wild due to their evolutionary progression, which poses a problem when placed in captivity. These rhinoceroses can overload on iron, which leads to build up in the lungs, liver, spleen and small intestine. Not only do these rhinoceros face threats being in the wild, but in captivity too. Black rhinoceros have become more susceptible to disease in captivity with high rates of mortality.
Illegal poaching for the international rhino horn trade is the main and most detrimental threat. The killing of these animals is not unique to modern-day society. The Chinese have maintained reliable documents of these happenings dating back to 1200 B.C. The ancient Chinese often hunted rhino horn for the making of wine cups, as well as the rhino's skin to manufacture imperial crowns, belts and armor for soldiers. A major market for rhino horn has historically been in the Middle East nations to make ornately carved handles for ceremonial daggers called jambiyas. Demand for these exploded in the 1970s, causing the black rhinoceros population to decline 96% between 1970 and 1992. The horn is also used in traditional Chinese medicine, and is said by herbalists to be able to revive comatose patients, facilitate exorcisms and various methods of detoxification, and cure fevers. It is also hunted for the Chinese superstitious belief that the horns allow direct access to Heaven due to their unique location and hollow nature. The purported effectiveness of the use of rhino horn in treating any illness has not been confirmed, or even suggested, by medical science. In June 2007, the first-ever documented case of the medicinal sale of black rhino horn in the United States (confirmed by genetic testing of the confiscated horn) occurred at a traditional Chinese medicine supply store in Portland, Oregon's Chinatown.
Reference: Wikipedia
Photo: AfricanConservation, J. J. Hornung, Christian Science Monitor