NAMES
TAXONOMY
Genus species (Animalia): Junco hyemalis
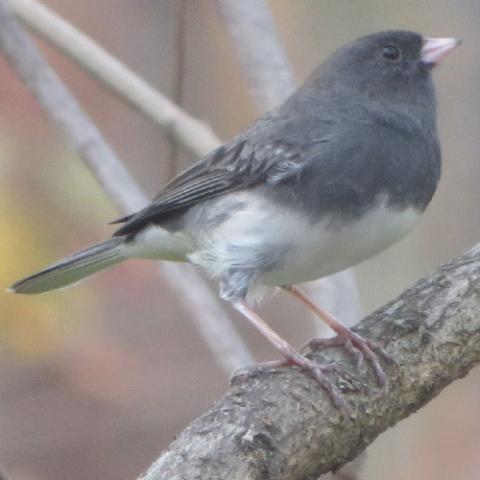
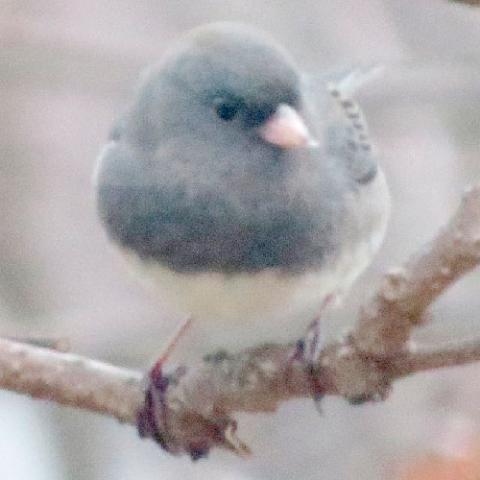
The dark-eyed junco (Junco hyemalis) is a species of junco, a group of small, grayish New World sparrows. The species is common across much of temperate North America and in summer it ranges far into the Arctic. It is a variable species, much like the related fox sparrow (Passerella iliaca), and its systematics are still not completely resolved.
Taxonomy
The dark-eyed junco was formally described by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in his landmark 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae as Fringilla hyemalis. The description consisted merely of the laconic remark "F[ringilla] nigra, ventre albo. ("A black 'finch' with white belly") and a statement that it came from America. Linnaeus based his description on the "Snow-Bird" that Mark Catesby had described and illustrated in his 1731 The Natural History of Carolina, Florida and the Bahama Islands.
The Bill of this Bird is white: The Breast and Belly white. All the rest of the Body black; but in some places dusky, inclining to Lead-color. In Virginia and Carolina they appear only in Winter: and in Snow they appear most. In Summer none are seen. Whether they retire and breed in the North (which is most probable) or where they go, when they leave these Countries in Spring, is to me unknown.
The type locality was restricted to South Carolina by the American Ornithologists' Union in 1931. The dark-eyed junco is now placed in the genus Junco that was introduced in 1831 by the German naturalist Johann Georg Wagler. The genus name Junco is the Spanish word for rush, from the Latin word juncus. Its modern scientific name means "winter junco", from the Latin word hyemalis "of the winter".
Distribution and habitat
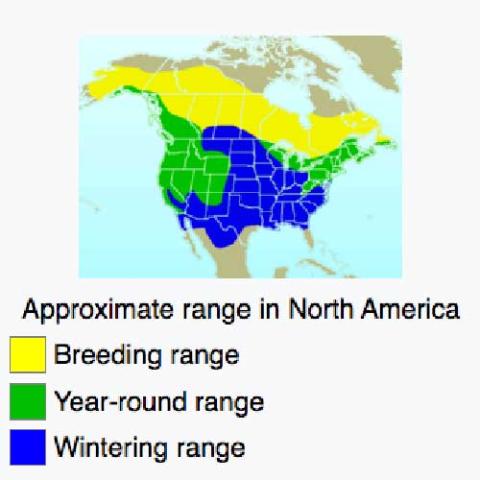
The dark-eyed junco's breeding habitat is coniferous or mixed forest areas throughout North America. In otherwise optimal conditions it also utilizes other habitats, but at the southern margin of its range it can only persist in its favorite habitat. Northern birds migrate further south, arriving in their winter quarters between mid-September and November and leaving to breed from mid-March onwards, with almost all of them gone by the end of April or so. Many populations are permanent residents or altitudinal migrants, while in cold years they may choose to stay in their winter range and breed there. For example, in the Sierra Nevada Mountains of eastern California, J. hyemalis populations will migrate to winter ranges 5,000–7,000 feet (1,500–2,100 m) lower than their summer range. Seasonally sympatric females show difference in migration and reproductive timing that is dependent on hormone and ovary regulation. The migrant female Junco hyemails experience delayed growth in the gonad to allow time for their seasonal migration. They then migrate down to the northeastern United States, where the resident subspecies is the Carolina dark-eyed junco (J. h. carolinensis). Female Carolina dark-eyed juncos have large ovaries and, therefore, do not experience gonadal growth delays because they are residents in the area. In winter, dark-eyed juncos are familiar in and around towns, and in many places are the most common birds at feeders. The slate-colored dark-eyed junco (J. h. hyemalis) is a rare vagrant to Western Europe and may successfully winter in Great Britain, usually in domestic gardens.
Behavior and ecology
These birds forage on the ground. In winter, they often forage in flocks that may contain several different subspecies. They mainly eat seeds, supplemented by the occasional insect. A flock of dark-eyed juncos has been known to be called a blizzard.
Breeding
Dark-eyed juncos usually nest in a cup-shaped depression on the ground, well hidden by vegetation or other material, although nests are sometimes found in the lower branches of a shrub or tree. The nests have an outer diameter of about 10 cm (3.9 in) and are lined with fine grasses and hair. Normally two clutches of four eggs are laid during the breeding season. The slightly glossy eggs are grayish or pale bluish-white and heavily spotted (sometimes splotched) with various shades of brown, purple or gray. The spotting is concentrated at the large end of the egg. The eggs are incubated by the female for 12 to 13 days. The young leave the nest between 11 and 14 days after hatching.
Juncos are the "snowbirds" of the middle latitudes. Over most of the eastern United States, they appear as winter sets in and then retreat northward each spring. Some juncos in the Appalachian Mountains remain there all year round, breeding at the higher elevations. These residents have shorter wings than the migrants that join them each winter. Longer wings are better suited to flying long distances, a pattern commonly noted among other studies of migratory vs. resident species.
The Dark-eyed Junco is one of the most common birds in North America and can be found across the continent, from Alaska to Mexico, from California to New York. A recent estimate set the junco’s total population at approximately 630 million individuals.
The oldest recorded Dark-eyed Junco was at least 11 years, 4 months old when it was recaptured and rereleased during banding operations in West Virginia in 2001. It had been banded in the same state in 1991.
Reference: Wikipedia, The Cornell Lab of Ornithology