NAMES
TAXONOMY
Upper Volta
Issued:
Stamp:
Kobus ellipsiprymnus
Angola
Issued:
Stamp:
Kobus ellipsiprymnus
Upper Volta
Issued:
Stamp:
Kobus ellipsiprymnus
Angola
Issued:
Stamp:
Kobus ellipsiprymnus
Upper Volta
Issued:
Stamp:
Kobus ellipsiprymnus
Angola
Issued:
Stamp:
Kobus ellipsiprymnus
Genus species (Animalia): Kobus ellipsiprymnus (Ellipsen waterbuck)
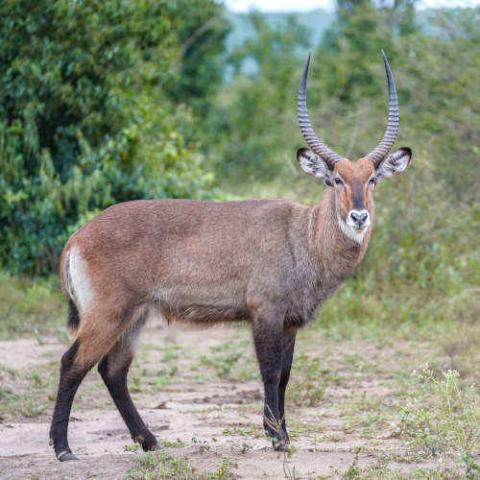
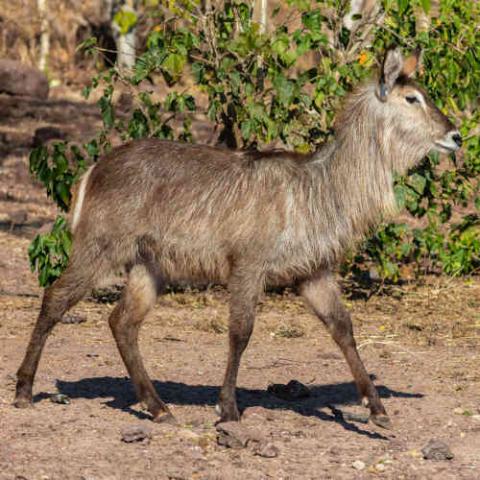
The Ellipsen waterbuck (Kobus ellipsiprymnus) is a large antelope found widely in sub-Saharan Africa. It is placed in the genus Kobus of the family Bovidae. It was first described by Irish naturalist William Ogilby in 1833. Its 13 subspecies are grouped under two varieties: the common or ellipsiprymnus waterbuck and the defassa waterbuck. The head-and-body length is typically between 177 and 235 cm (70 and 93 in) and the typical height is between 120 and 136 cm (47 and 54 in). In this sexually dimorphic antelope, males are taller and heavier than females. Males reach roughly 127 cm (50 in) at the shoulder, while females reach 119 cm (47 in). Males typically weigh 198–262 kg (437–578 lb) and females 161–214 kg (355–472 lb). Their coat color varies from brown to grey. The long, spiral horns, present only on males, curve backward, then forward, and are 55–99 cm (22–39 in) long.
Waterbucks are rather sedentary in nature. As gregarious animals, they may form herds consisting of six to 30 individuals. These groups are either nursery herds with females and their offspring or bachelor herds. Males start showing territorial behaviour from the age of 5 years, but are most dominant from the six to nine. The waterbuck cannot tolerate dehydration in hot weather, and thus inhabits areas close to sources of water. Predominantly a grazer, the waterbuck is mostly found on grassland. In equatorial regions, breeding takes place throughout the year, but births are at their peak in the rainy season. The gestational period lasts 7–8 months, followed by the birth of a single calf.
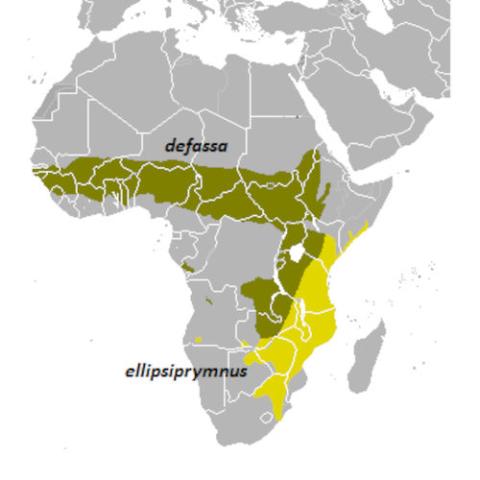
Waterbucks inhabit scrub and savanna areas along rivers, lakes, and valleys. Due to their requirement for grasslands and water, waterbucks have a sparse ecotone distribution. The IUCN lists the waterbuck as being of least concern. More specifically, the common waterbuck is listed as of least concern. while the defassa waterbuck is near threatened. The population trend for both is downwards, especially that of the defassa, with large populations being eliminated from certain habitats because of poaching and human disturbance.
Taxonomy and etymology
The scientific name of the waterbuck is Kobus ellipsiprymnus. The waterbuck is one of the six species of the genus Kobus in the family Bovidae. It was first described by Irish naturalist William Ogilby in 1833. The generic name Kobus is a Neo-Latin word, originating from an African name, koba. The specific name ellipsiprymnus refers to the white, elliptical ring on the rump, from the Greek ellipes (ellipse) and prymnos (prumnos, hind part). The animal acquired the vernacular name "waterbuck" due to its heavy dependence on water as compared to other antelopes and its ability to enter into water for defense.
The type specimen of the waterbuck was collected by South African hunter-explorer Andrew Steedman in 1832. This specimen was named Antilope ellipsiprymnus by Ogilby in 1833. This species was transferred to the genus Kobus in 1840, becoming K. ellipsiprymnus. It is usually known as the common waterbuck. In 1835, German naturalist Eduard Rüppell collected another specimen, which differed from Steedman's specimen in having a prominent white ring on its rump. Considering it a separate species, Rüppell gave it the Amharic name "defassa" waterbuck and scientific name Antilope defassa. Modern taxonomists, however, consider the common waterbuck and the defassa waterbuck a single species, K. ellipsiprymnus, given the large number of instances of hybridisation between the two. Interbreeding between the two takes place in the Nairobi National Park owing to extensive overlapping of habitats. Though both groups occur in Zambia as well, their ranges are separated by relief features or by the Muchinga escarpment.
Description
The waterbuck is the largest amongst the six species of Kobus. It is a sexually dimorphic antelope, with the males nearly 7% taller than females and around 8% longer. The head-and-body length is typically 177–235 cm (70–93 in) and the typical height is 120–136 cm (47–54 in). Males reach approximately 127 cm (50 in) at the shoulder, while females reach 119 cm (47 in). The waterbuck is one of the heaviest antelopes. A newborn typically weighs 13.6 kg (30 lb), and growth in weight is faster in males than in females. Males typically weigh 198–262 kg (437–578 lb) and females 161–214 kg (355–472 lb). The tail is 22–45 cm (8.7–17.7 in) long.
The waterbuck has a robust build. The shaggy coat is reddish brown to grey, and becomes progressively darker with age. Males are darker than females. Though apparently thick, the hair is sparse on the coat. The hair on the neck is, however, long and shaggy. When sexually excited, the skin of the waterbuck secretes a greasy substance with the odour of musk (sebum), giving it the name "greasy kob". The odor of this is so unpleasant that it repels predators. This secretion also assists in water-proofing the body when the animal dives into water. The facial features include a white muzzle and light eyebrows and lighter insides of the ears. A cream-colored patch (called "bib") is on the throat. Waterbuck are characterized by a long neck and short, strong, black legs. Females have two nipples. Preorbital glands, foot glands, and inguinal glands are absent.
The ellipsen waterbuck and the defassa waterbuck are remarkably different in their physical appearances. Measurements indicate greater tail length in the latter, whereas the ellipsen waterbuck stands taller than the defassa waterbuck. However, the principal differentiation between the two types is the white ring of hair surrounding the tail on the rump, which is a hollow circle in the ellipsen waterbuck, but covered with white hair in the defassa waterbuck.
The long, spiral horns curve backward, then forward. Found only on males, the horns range from 55 to 99 cm (22 to 39 in) in length. To some extent, the length of the horns is related to the bull's age. A rudimentary horn in the form of a bone lump may be found on the skulls of females.
Diet
The waterbuck exhibits great dependence on water. It can not tolerate dehydration in hot weather, and thus inhabits areas close to sources of water. However, it has been observed that unlike the other members of its genus (such as the kob and puku), the waterbuck ranges farther into the woodlands while maintaining its proximity to water. With grasses constituting a substantial 70 to 95 percent of the diet, the waterbuck is predominantly a grazer frequenting grasslands. Reeds and rushes like Typha and Phragmites may also be preferred. A study found regular consumption of three grass species round the year: Panicum anabaptistum, Echinochloa stagnina and Andropogon gayanus. Hyparrhenia involucrata, Acroceras amplectens and Oryza barthii along with annual species were the main preference in the early rainy season, while long life grasses and forage from trees constituted three-fourths of the diet in the dry season.
Though the defassa waterbuck was found to have a much greater requirement for protein than the African buffalo and the Beisa oryx, the waterbuck was found to spend much less time on browsing (eating leaves, small shoots, and fruits) in comparison to the other grazers. In the dry season, about 32% of the 24-hour day was spent in browsing, whereas no time was spent on it during the wet season. The choice of grasses varies with location rather than availability; for instance, in western Uganda, while Sporobolus pyramidalis was favoured in some places, Themeda triandra was the main choice elsewhere. The common waterbuck and the defassa waterbuck in the same area may differ in their choices; while the former preferred Heteropogon contortus and Cynodon dactylon, the latter showed less preference for these grasses.
Reference: Wikipedia
Photo: commons.wikimedia.org (Giles Laurent), commons.wikimedia.org (Diego Delso), commons.wikimedia.org (Chrysaetus)