NAMES
TAXONOMY
South Africa
Issued:
Stamp:
Taurotragus oryx
Burundi
Issued:
Stamp:
Taurotragus oryx
Angola
Issued:
Stamp:
Taurotragus oryx
South Africa
Issued:
Stamp:
Taurotragus oryx
Burundi
Issued:
Stamp:
Taurotragus oryx
Angola
Issued:
Stamp:
Taurotragus oryx
South Africa
Issued:
Stamp:
Taurotragus oryx
Burundi
Issued:
Stamp:
Taurotragus oryx
Angola
Issued:
Stamp:
Taurotragus oryx
Genus species: Taurotragus oryx
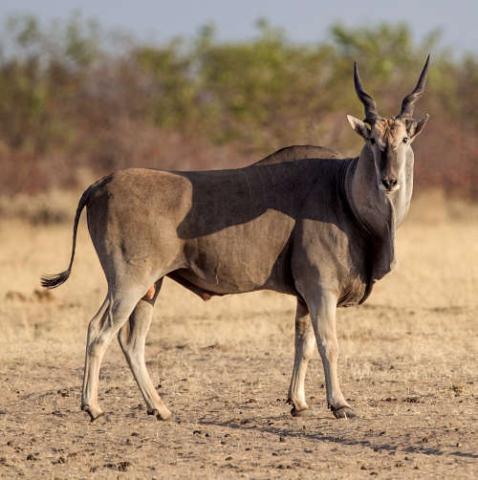
The common eland (Taurotragus oryx), also known as the southern eland or eland antelope, is a large-sized savannah and plains antelope found in East and Southern Africa. An adult male is around 1.6 m (5.2 ft) tall at the shoulder (females are 20 cm (7.9 in) shorter) and can weigh up to 942 kg (2,077 lb) with a typical range of 500–600 kg (1,100–1,300 lb), 340–445 kg (750–981 lb) for females).
It is the second-largest antelope in the world, being slightly smaller on average than the giant eland. It was scientifically described by Peter Simon Pallas in 1766.
Mainly a herbivore, its diet is primarily grasses and leaves. Common elands form herds of up to 500 animals, but are not territorial. The common eland prefers habitats with a wide variety of flowering plants such as savannah, woodlands, and open and montane grasslands; it avoids dense forests. It uses loud barks, visual and postural movements, and the flehmen response to communicate and warn others of danger. The common eland is used by humans for leather, and meat and has been domesticated in southern Africa. Eland milk contains more butterfat than cow's milk, and can keep longer without pasteurizing.
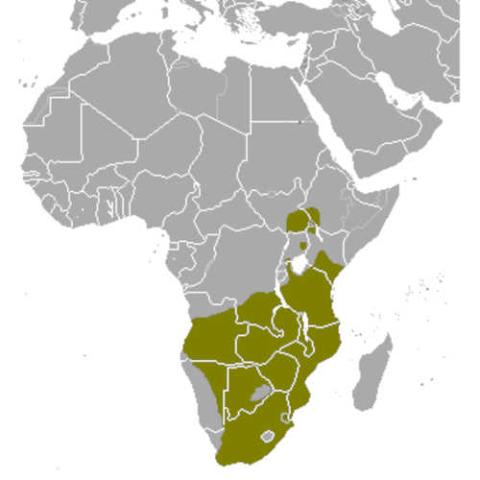
It is native to Angola, Botswana, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Kenya, Lesotho, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, Rwanda, South Africa, South Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, and Zimbabwe, but is no longer present in Burundi. While the common eland's population is decreasing, it is classified as of least concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
Etymology
The scientific name of the common eland is Taurotragus oryx, composed of three words: tauros, tragos, and oryx. Tauros is Greek for a bull or bullock, meaning the same as the Latin taurus. Tragos is Greek for a male goat, referring to the tuft of hair that grows in the eland's ear and its resemblance to a goat's beard. Oryx is Latin and Greek (genitive: orygos) for pickaxe, referring to the pointed horns of North African antelopes like the common eland and scimitar-horned oryx.
The name "eland" is Afrikaans for "elk" or "moose". It has a Baltic source similar to the Lithuanian élnis, which means "deer". It was borrowed earlier as ellan (French) in the 1610s or Elend (German). When Dutch settlers came to the Cape of Good Hope, creating the Dutch Cape Colony, they named the animal after the large, herbivorous moose. In Dutch, the animal is called "eland antelope" to distinguish it from the moose, which is found in the northern boreal forests.
Physical description
Common elands are spiral-horned antelopes. They are sexually dimorphic, with females being smaller than the males. Females weigh 300–600 kg (660–1,320 lb), measure 200–280 cm (79–110 in) from the snout to the base of the tail and stand 125–153 cm (49–60 in) at the shoulder. Bulls weigh 400–942 kg (882–2,077 lb), are 240–345 cm (94–136 in) from the snout to the base of the tail and stand 150–183 cm (59–72 in) at the shoulder. The tail is 50–90 cm (20–35 in) long. Male elands can weigh up to 1,000 kg (2,200 lb).
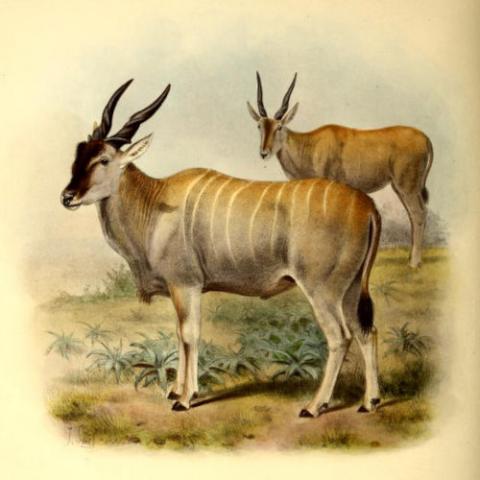
Their coat differs geographically, with elands in northern part of their range having distinctive markings (torso stripes, markings on legs, dark garters and a spinal crest) that are absent in the south. Apart from a rough mane, the coat is smooth. Females have a tan coat, while the coats of males are darker, with a bluish-grey tinge. Bulls may also have a series of vertical white stripes on their sides (mainly in parts of the Karoo in South Africa). As males age, their coat becomes more grey. Males also have dense fur on their foreheads and a large dewlap on their throats.
Both sexes have horns with a steady spiral ridge (resembling that of the bushbuck). The horns are visible as small buds in newborns and grow rapidly during the first seven months. The horns of males are thicker and shorter than those of females (males' horns are 43–66 cm (17–26 in) long and females' are 51–69 cm (20–27 in) long), and have a tighter spiral. Males use their horns during rutting season to wrestle and butt heads with rivals, while females use their horns to protect their young from predators.
The common eland is the slowest antelope, with a peak speed of 40 km/h (25 mph) that tires them quickly. However, they can maintain a 22 km/h (14 mph) trot indefinitely. Elands are capable of jumping up to 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in) from a standing start when startled (up to 3 m (9.8 ft) for young elands). The common eland's life expectancy is generally between 15 and 20 years; in captivity, some live up to 25 years.
Eland herds are accompanied by a loud clicking sound that has been subject to considerable speculation. The weight of the animal may cause the two halves of its hooves to splay apart, and the clicking is the result of the hoof snapping together when the animal raises its leg. The sound carries some distance from a herd, and may be a form of communication.
Taxonomy
The common eland was first described in 1766 by German zoologist and botanist Peter Simon Pallas. It belongs to the order Artiodactyla, family Bovidae, and subfamily Bovinae. Common elands are sometimes considered part of the genus Tragelaphus on the basis of molecular phylogenetics, but are usually categorized as Taurotragus, along with the giant eland (T. derbianus).
Subspecies
Three subspecies of common elands have been recognized, though their validity has been disputed.
- T. o. oryx (Pallas, 1766; Cape eland): also called alces, barbatus, canna and oreas. It is found in Southern and southwestern Africa. The fur is tawny and adults lose their stripes.
- T. o. livingstonii (Sclater, 1864; Livingstone's eland): also called kaufmanni, niediecki, selousi and triangularis. It is found in the Central Zambezian miombo woodlands. Livingstone's eland has brown fur with up to 12 stripes.
- T. o. pattersonianus (Lydekker, 1906; East African eland or Patterson's eland): also called billingae. It is found in East Africa, hence its common name. Like Livingstone's eland, its fur can also have up to 12 stripes.
Found by and named after John Henry Patterson, who describes the specimen in The Man-eaters of Tsavo (1907).
Habitat and distribution
Common elands live on the open plains of Southern Africa and along the foothills of the great southern African plateau. The species extends north into Ethiopia and most arid zones of South Sudan, west into eastern Angola and Namibia, and south to South Africa. However, a low density of elands exists in Africa due to poaching and human settlement.
Elands prefer to live in semiarid areas that contain many shrub-like bushes, and often inhabit grasslands, woodlands, subdesert, bush, and mountaintops with altitudes of about 15,000 ft (4,600 m). Elands do, however, avoid forests, swamps and deserts. The places inhabited by elands generally contain Acacia, Combretum, Commiphora, Diospyros, Grewia, Rhus, and Ziziphus trees and shrubs; some of these also serve as their food.
Eland can be found in many national parks and reserves today, including Nairobi National Park and Tsavo East National Park, Tsavo West National Park, Masai Mara National Reserve, (Kenya); Serengeti National Park, Ruaha National Park and Tarangire National Park, Ngorongoro Crater, (Tanzania); Kagera National Park (Rwanda); Nyika National Park (Malawi); Lake Mburo National Park (Uganda); Kidepo Valley National Park (Uganda); Luangwa Valley and Kafue National Park (Zambia); Hwange National Park, Matobo National Park, Tuli Safari Area and Chimanimani Eland Sanctuary (Zimbabwe); Kruger National Park, Kgalagadi Transfrontier Park, Giant's Castle and Suikerbosrand NR (South Africa).
They live on home ranges that can be 200–400 km2 for females and juveniles and 50 km2 for males.
Habitat and distribution
Common elands live on the open plains of Southern Africa and along the foothills of the great southern African plateau. The species extends north into Ethiopia and most arid zones of South Sudan, west into eastern Angola and Namibia, and south to South Africa. However, a low density of elands exists in Africa due to poaching and human settlement.
Elands prefer to live in semiarid areas that contain many shrub-like bushes, and often inhabit grasslands, woodlands, subdesert, bush, and mountaintops with altitudes of about 15,000 ft (4,600 m). Elands do, however, avoid forests, swamps and deserts. The places inhabited by elands generally contain Acacia, Combretum, Commiphora, Diospyros, Grewia, Rhus, and Ziziphus trees and shrubs; some of these also serve as their food.
Eland can be found in many national parks and reserves today, including Nairobi National Park and Tsavo East National Park, Tsavo West National Park, Masai Mara National Reserve, (Kenya); Serengeti National Park, Ruaha National Park and Tarangire National Park, Ngorongoro Crater, (Tanzania); Kagera National Park (Rwanda); Nyika National Park (Malawi); Lake Mburo National Park (Uganda); Kidepo Valley National Park (Uganda); Luangwa Valley and Kafue National Park (Zambia); Hwange National Park, Matobo National Park, Tuli Safari Area and Chimanimani Eland Sanctuary (Zimbabwe); Kruger National Park, Kgalagadi Transfrontier Park, Giant's Castle and Suikerbosrand NR (South Africa).
They live on home ranges that can be 200–400 km2 for females and juveniles and 50 km2 for males.
Ecology and behavior
Common elands are nomadic and crepuscular. They eat in the morning and evening, rest in shade when hot, and remain in sunlight when cold. They are commonly found in herds numbering up to 500, with individual members remaining in the herd from several hours to several months. Juveniles and mothers tend to form larger herds, while males may separate into smaller groups or wander individually. During estrus, mainly in the rainy season, groups tend to form more regularly. In Southern Africa, common elands will often associate with herds of zebras, roan antelopes and oryxes.
Common elands communicate via gestures, vocalizations, scent cues, and display behaviors. The flehmen response also occurs, primarily in males in response to contact with female urine or genitals. Females urinate to indicate fertility during the appropriate phase of their estrous cycle, as well as to indicate their lack of fertility when harassed by males. If eland bulls find any of their predators nearby, they bark and attempt to attract the attention of others by trotting back and forth until the entire herd is conscious of the danger. Some of their main predators include lions, African wild dogs, cheetahs, and spotted hyenas. Eland calves are more vulnerable than adults to their predators.
Interaction with humans
Currently, common elands are not endangered. They are conserved by the United States Endangered Species Act, and regulated in international trade by the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species. Using ground counts and aerial surveys, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) calculates the population density of the common eland to be between 0.05 and 1 per square kilometre with a total population estimate of 136,000. Populations are considered stable or increasing in the countries of Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, South Africa, Malawi, Kenya and Tanzania.
The population is, however, gradually decreasing due to habitat loss, caused by expanding human settlements and poaching for its superior meat. As they are docile and inactive most of the time, they can easily be killed. The species became extinct in Eswatini and Zimbabwe, but has been reintroduced.
The IUCN states that about half of the estimated total population lives in protected areas and 30% on private land. Protected areas that support major populations include Omo (Ethiopia), Serengeti, Katavi, Ruaha, and Selous-Kilombero (Tanzania), Kafue and North Luangwa (Zambia), Nyika (Malawi), Etosha (Namibia), Kgalagadi Transfrontier Park (Botswana/South Africa) and Ukhahlamba Drakensberg Park (South Africa). Most of these populations appear to be stable. Relatively large numbers of common elands now live on private land, particularly in Namibia, Zimbabwe, and South Africa, reflecting its value as a trophy animal. Common elands have also been widely domesticated in Zimbabwe, South Africa.
Reference: Wikipedia
Photo: Yathin S Krishnappa