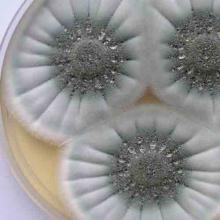
Penicillium roqueforti
Common name:
Roquefort cheese
Genus:
Penicillium
Family:
Tricholomataceae
Order:
Eurotiales
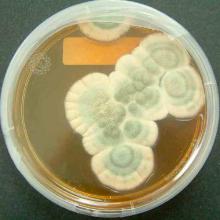
Penicillium chrysogenum
Common name:
Penicillin
Genus:
Penicillium
Family:
Tricholomataceae
Order:
Eurotiales
Penicillium roqueforti
Common name:
Roquefort cheese
Genus:
Penicillium
Family:
Tricholomataceae
Order:
Eurotiales
Penicillium chrysogenum
Common name:
Penicillin
Genus:
Penicillium
Family:
Tricholomataceae
Order:
Eurotiales
Penicillium roqueforti
Common name:
Roquefort cheese
Genus:
Penicillium
Family:
Tricholomataceae
Order:
Eurotiales
Penicillium chrysogenum
Common name:
Penicillin
Genus:
Penicillium
Family:
Tricholomataceae
Order:
Eurotiales
Genus (Fungi): Penicillium
Penicillium (/ˌpɛnɪˈsɪliəm/) is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that is of major importance in the natural environment, in food spoilage, and in food and drug production.
Some members of the genus produce penicillin, a molecule that is used as an antibiotic, which kills or stops the growth of certain kinds of bacteria. Other species are used in cheesemaking. According to the Dictionary of the Fungi (10th edition, 2008), the widespread genus contains over 300 species.
Characteristics
The thallus (mycelium) consists of highly branched networks of multinucleated,usually colourless hyphae, with each pair of cells separated by a septum. Conidiophores are at the end of each branch accompanied by green spherical constricted units called conidia. These propagules lay a significant role in reproduction; conidia are the main dispersal strategy of these fungi.
Sexual reproduction involves the production of ascospores, commencing with the fusion of an archegonium and an antheridium, with sharing of nuclei. The irregularly distributed asci contain eight unicellular ascospores each.
Reference: Wikipedia